ZebraPose: Zebra Detection and Pose Estimation using only Synthetic Data
Elia Bonetto2,1,* Aamir Ahmad1,2
1University of Stuttgart 2Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems
* Corresponding Author

Introduction
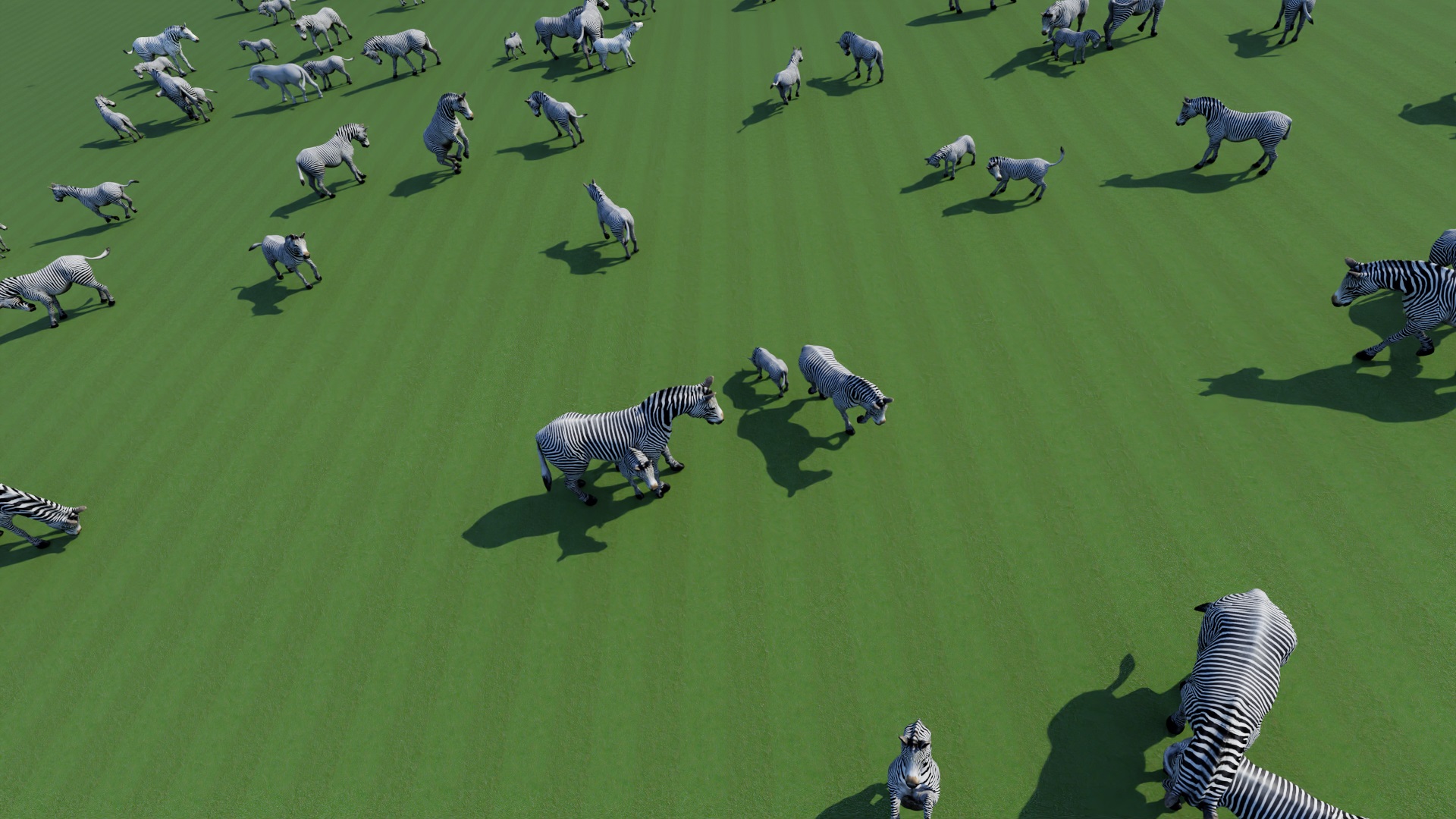
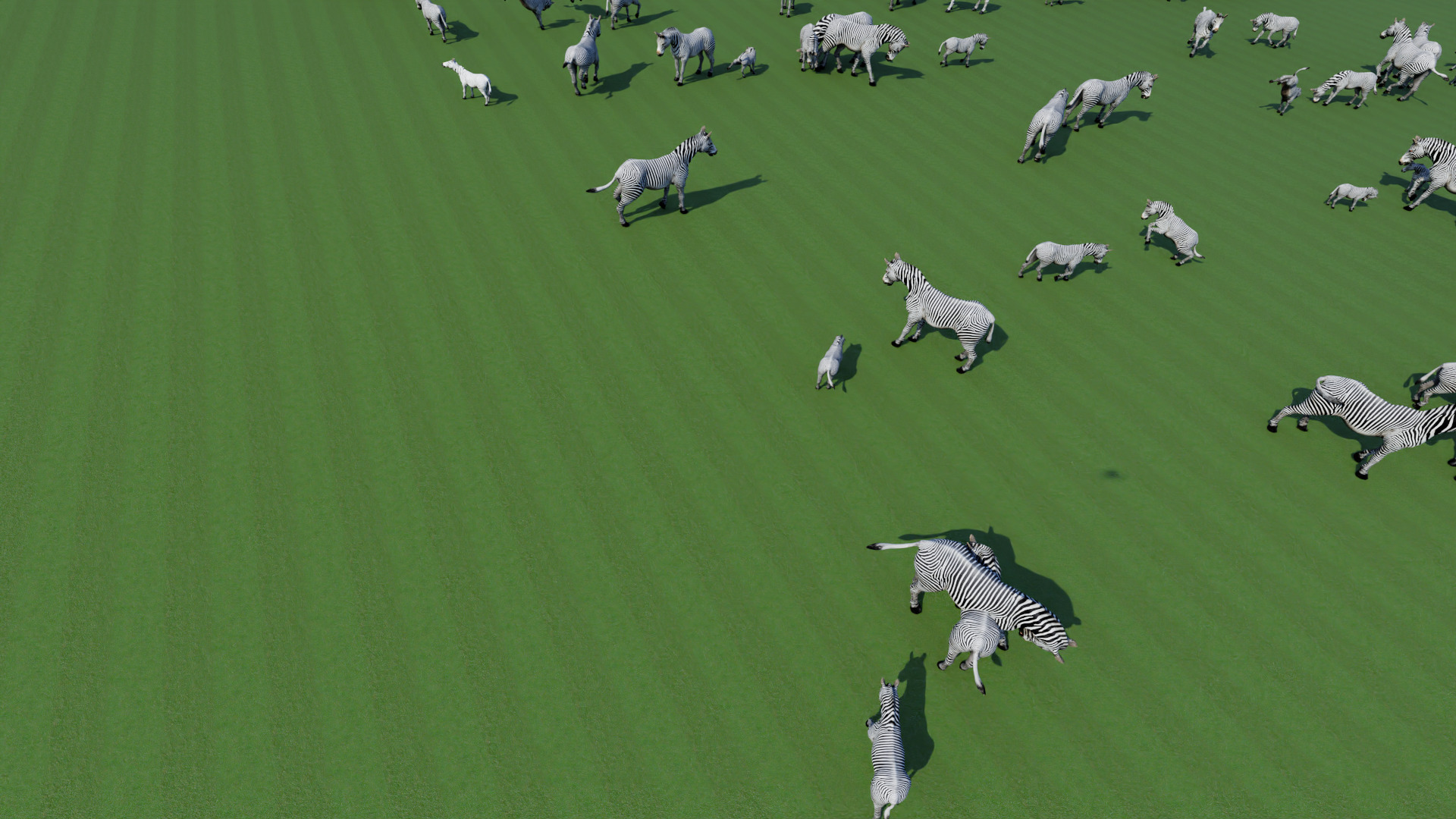
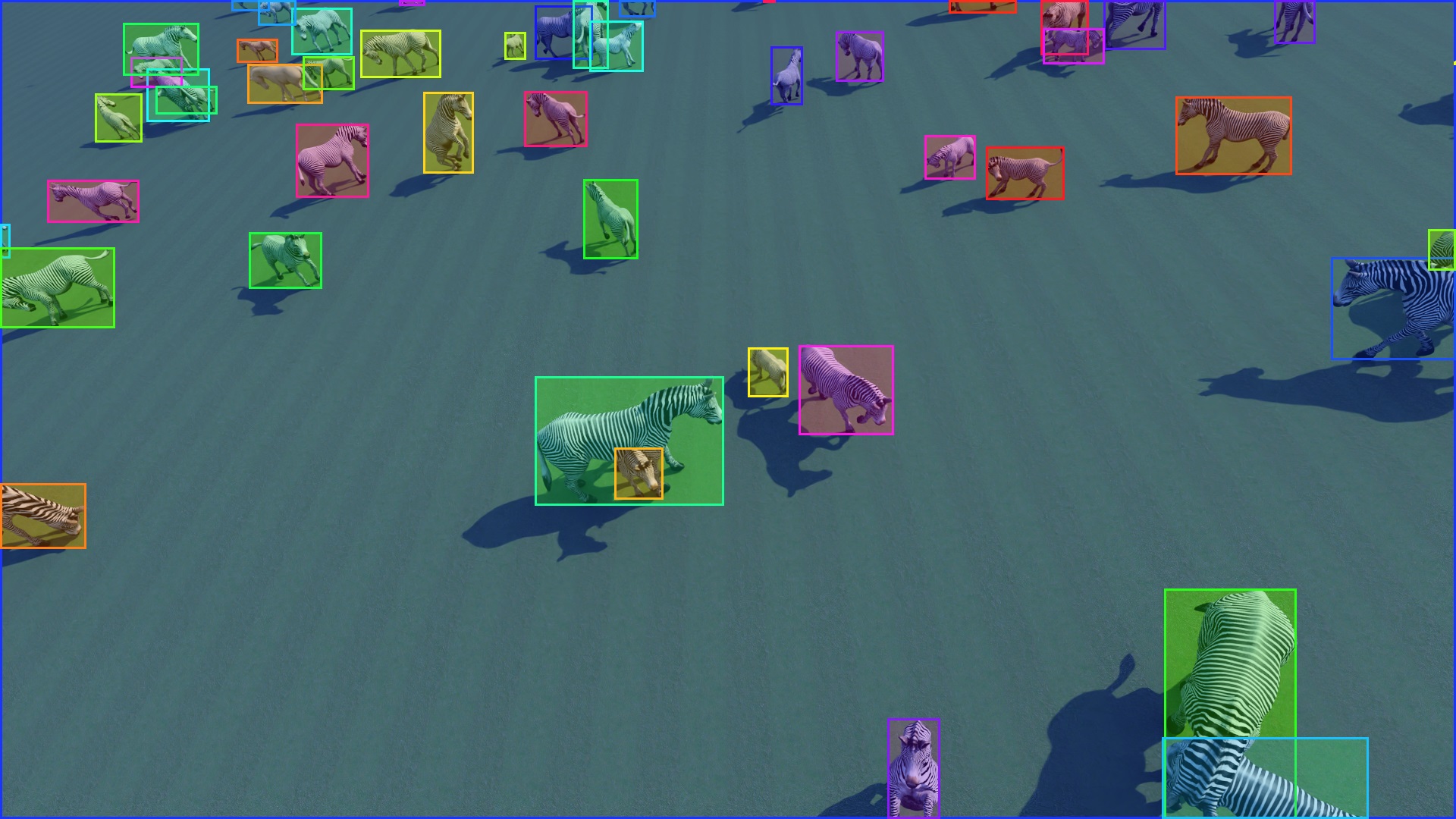
In this project we use GRADE to generate synthetic data and learn to detect and estimate the 2D pose of zebras. We did that by using a variety of environments from Unreal Engine, a freely available zebra model. We, obtained an outdoor synthetic Zebra datasets observed from multiple aerial views. We demonstrated that generating synthetic data using GRADE can give us visual-realistic information that can be used directly to train detection and 2D pose estimation models that will work on real-world images without any fine-tuning or usage of labelled real-world data.
In our first project we trained a detector of zebras from aerial point of views using only synthetic images. With ZebraPose we extend that to both commonly available images and to the task of 2D pose estimation, thus obtaining a full top-down system learned solely from synthetic data.
Abstract:
Synthetic data is increasingly being used to address the lack of labeled images in uncommon domains for deep learning tasks. A prominent example is 2D pose estimation of animals, particularly for wild species such as zebras. However, many approaches still require real-world data, consistency and style constraints, sophisticated animal models, and/or powerful pre-trained networks to bridge the syn-to-real gap. Moreover, they often assume that the animal can be reliably detected in images or videos, a hypothesis that often does not hold, e.g. in wildlife scenarios or aerial images. To solve this, we use synthetic data generated with a 3D photorealistic simulator to obtain the first synthetic dataset that can be used for both detection and 2D pose estimation of zebras without applying any of the aforementioned bridging strategies. Unlike previous works, we extensively train and benchmark our detection and 2D pose estimation models on multiple real-world and synthetic datasets using both pre-trained and non-pre-trained backbones. These experiments show how the models trained from scratch and only with synthetic data can consistently generalize to real-world images of zebras in both tasks. Moreover, we show it is possible to easily generalize those same models to 2D pose estimation of horses with a minimal amount of real-world images to account for the domain transfer.
Examples of our synthetic Zebras dataset
From Synthetic Data-based Detection of Zebras in Drone Imagery, IEEE European Conference on Mobile Robots 2023, Bonetto et al., 2023.
Contact
Questions: zebrapose@tue.mpg.de
Licensing: ps-licensing@tue.mpg.de